Progress in development of portable biosensors for rapid and in-field detection of antibiotic residues in poultry:
On the basis of the phase I of the project, a fluorescence biosensing technology and relevant automatic equipment were further designed and developed aiming to simultaneously detection of a variety of antibiotics residues. In terms of detection technology, the simultaneous detection of enrofloxacin, sulfanilamide and erythromycin have been preliminarily completed. In the proof-of-principle part, 623 nm QDs with the highest fluorescence efficiency was used, and every single type of antibiotic was detected under the same condition (pH 7.4 at room temperature). when detecting sulfamethazine, after replacing quantum dots and optimizing dosage of QDs and MBs in modification and detection steps, the initial results were satisfactory. In terms of equipment, the magnetic separation pre-processing automation equipment version 1.0 for enrofloxacin was developed (Figure 1), which can process the standard sample within 50 minutes. The fluorescence value of the test results showed that the coefficient of variation between groups was within 10%, and the minimum detection limit was 54 ng/ml. The next step is to realize simultaneous detection of three antibiotics and then combine with equipment testing.
During this period, the group was keeping close touch with the NewHope Company to get demand analysis and suggestion based on their production. Moreover, the group also built new collaboration with research group and company. Recently, the group has started the collaboration with the group of Academician Jianzhong Sheng and gotten support of antibiotics detection materials and suggestions. The group also made efforts to propagandize for the project and Walmart. On March 21, 2020, Prof. Fu gave a lecture for undergraduates of Hunan University of Science and Technology. Prof. Fu introduced the project and highlighted the efforts of Walmart devoting to food safety (Figure 2).
Recently, the group developed a new biosensing technology based on electrochemical conversion of magnetic nanoparticles. The study has published a research article in journal of Electroanalysis. This study is promising for the label-free and rapid detection of antibiotics and currently it has been adopted in enoxacin detection.
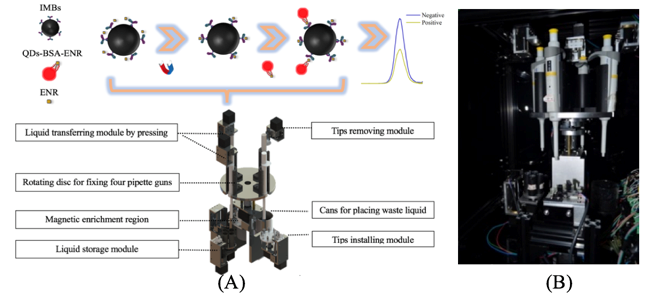
Figure 1. (A) functions of automated separation device and (B) the inside view of automated separation device.

Figure 2. PPT slides of Prof. Fu for the lecture to Hunan University of Science and Technology.
Publication: Yawen He, Fei Jia, Junfei Guan, Yingchun Fu, Yanbin Li, Electrochemical Conversion of Magnetic Nanoparticles Using Disposable Working Electrode in a 3D‐Printed Electrochemical Cell, Electroanalysis, 2020, in press.